Introduction
The epoch contract stores a lot of different state, and the state is constantly changing. As an external party, there are two ways to keep track of these state changes. You can either use Cadence scripts to query the state of the contract at any given time, or you can monitor events that are emitted by the epoch contract to be notified of any important occurrences.
Monitor Epoch Service Events
These events can be queried using the Go or JavaScript SDKs to extract useful notifications and information about the state of the epoch preparation protocol.
What is a Service Event?
Service events are special messages that are generated by smart contracts and included in execution results. They enable communication between system smart contracts and the Flow protocol. In other words, they serve as a communication mechanism between the execution state and the protocol state.
Concretely, service events are defined and emitted as events like any other in Cadence. An event is considered a service event when it is:
- emitted within the service chunk
- emitted from a smart contract deployed to the service account
- conformant to an event allowlist
Each block contains a system chunk. For each system chunk, all service events emitted are included in the corresponding execution result.
When verifying the system chunk, verifier nodes will only produce result approvals when the system chunks included in the execution result are correct. Thus, the security of this communication mechanism is enforced by the verification system.
When sealing a block containing a service event, the consensus committee will update the protocol state accordingly, depending on the semantics of the event.
For example, a service event may indicate that a node's stake has diminished to the point where they should be ejected, in which case the consensus committee would mark that node as ejected in the protocol state.
Service events are fundamentally asynchronous, due the lag between block execution and sealing. Consequently they are handled slightly differently than other protocol state updates.
The diagram below illustrates the steps each service event goes through to be included in the protocol state.
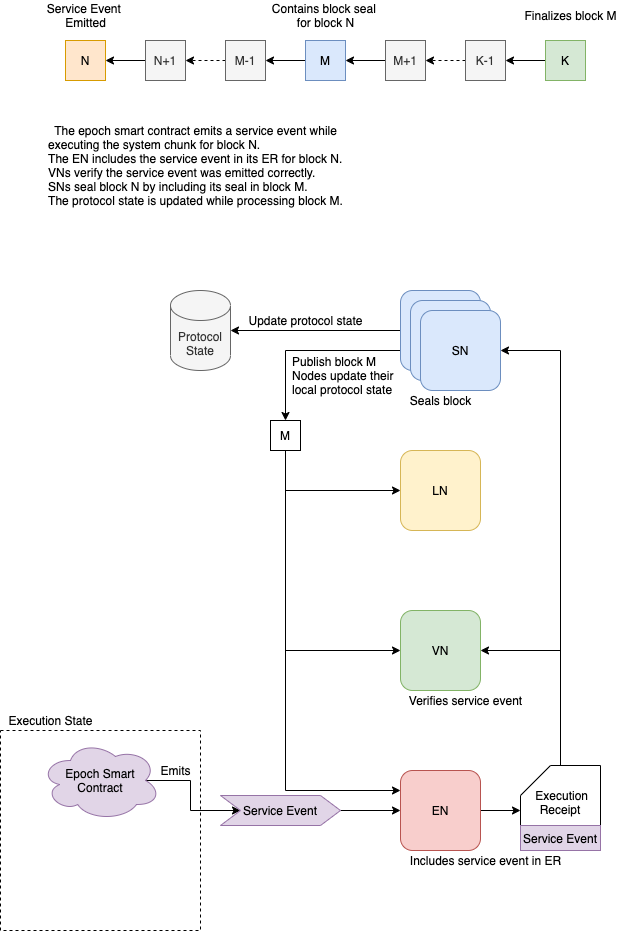
For conciseness, we say a service event is sealed when the block in which it was emitted is sealed,
and we say a service event is finalized when the block containing the seal is finalized.
Event Descriptions
FlowEpoch.EpochStart
The Epoch Start service event is emitted by FlowEpoch.startNewEpoch()
when the epoch commit phase ends and the Epoch Smart Contracts transition
to the staking auction phase.
It contains the relevant metadata for the new epoch that was generated during the last epoch:
_24 access(all) event EpochStart (_24_24 /// The counter for the current epoch that is beginning_24 counter: UInt64,_24_24 /// The first view (inclusive) of the current epoch._24 firstView: UInt64,_24_24 /// The last view (inclusive) of the current epoch's staking auction._24 stakingAuctionEndView: UInt64,_24_24 /// The last view (inclusive) of the current epoch._24 finalView: UInt64,_24_24 /// Total FLOW staked by all nodes and delegators for the current epoch._24 totalStaked: UFix64,_24_24 /// Total supply of all FLOW for the current epoch_24 /// Includes the rewards that will be paid for the previous epoch_24 totalFlowSupply: UFix64,_24_24 /// The total rewards that will be paid out at the end of the current epoch._24 totalRewards: UFix64,_24 )
FlowEpoch.EpochSetup
The Epoch Setup service event is emitted by FlowEpoch.startEpochSetup()
when the staking auction phase ends and the Epoch Smart Contracts transition to the Epoch Setup phase.
It contains the finalized identity table for the upcoming epoch,
as well as timing information for phase changes.
_35access(all) event EpochSetup (_35_35 /// The counter for the upcoming epoch. Must be one greater than the_35 /// counter for the current epoch._35 counter: UInt64,_35_35 /// Identity table for the upcoming epoch with all node information._35 /// Includes:_35 /// nodeID, staking key, networking key, networking address, role,_35 /// staking information, weight, and more._35 nodeInfo: [FlowIDTableStaking.NodeInfo],_35_35 /// The first view (inclusive) of the upcoming epoch._35 firstView: UInt64,_35_35 /// The last view (inclusive) of the upcoming epoch._35 finalView: UInt64,_35_35 /// The cluster assignment for the upcoming epoch. Each element in the list_35 /// represents one cluster and contains all the node IDs assigned to that_35 /// cluster, with their weights and votes_35 collectorClusters: [FlowClusterQC.Cluster],_35_35 /// The source of randomness to seed the leader selection algorithm with _35 /// for the upcoming epoch._35 randomSource: String,_35_35 /// The deadlines of each phase in the DKG protocol to be completed in the upcoming_35 /// EpochSetup phase. Deadlines are specified in terms of a consensus view number. _35 /// When a DKG participant observes a finalized and sealed block with view greater _35 /// than the given deadline, it can safely transition to the next phase. _35 DKGPhase1FinalView: UInt64,_35 DKGPhase2FinalView: UInt64,_35 DKGPhase3FinalView: UInt64_35)
FlowEpoch.EpochCommit
The EpochCommit service event is emitted when the Epoch Smart Contracts transition
from the Epoch Setup phase to the Epoch Commit phase.
It is emitted only when all preparation for the upcoming epoch (QC and DKG) has been completed.
_16access(all) event EpochCommit (_16_16 /// The counter for the upcoming epoch. Must be equal to the counter in the_16 /// previous EpochSetup event._16 counter: UInt64,_16_16 /// The result of the QC aggregation process. Each element contains _16 /// all the nodes and votes received for a particular cluster_16 /// QC stands for quorum certificate that each cluster generates._16 clusterQCs: [FlowClusterQC.ClusterQC],_16_16 /// The resulting public keys from the DKG process, encoded as by the flow-go_16 /// crypto library, then hex-encoded._16 /// Group public key is the first element, followed by the individual keys_16 dkgPubKeys: [String],_16)
Query Information with Scripts
The FlowEpoch smart contract stores important metadata about the current, proposed,
and previous epochs. Metadata for all historical epochs is stored permanently
in the Epoch Smart Contract's storage.
_38access(all) struct EpochMetadata {_38_38 /// The identifier for the epoch_38 access(all) let counter: UInt64_38_38 /// The seed used for generating the epoch setup_38 access(all) let seed: String_38_38 /// The first view of this epoch_38 access(all) let startView: UInt64_38_38 /// The last view of this epoch_38 access(all) let endView: UInt64_38_38 /// The last view of the staking auction_38 access(all) let stakingEndView: UInt64_38_38 /// The total rewards that are paid out for the epoch_38 access(all) var totalRewards: UFix64_38_38 /// The reward amounts that are paid to each individual node and its delegators_38 access(all) var rewardAmounts: [FlowIDTableStaking.RewardsBreakdown]_38_38 /// Tracks if rewards have been paid for this epoch_38 access(all) var rewardsPaid: Bool_38_38 /// The organization of collector node IDs into clusters_38 /// determined by a round robin sorting algorithm_38 access(all) let collectorClusters: [FlowClusterQC.Cluster]_38_38 /// The Quorum Certificates from the ClusterQC contract_38 access(all) var clusterQCs: [FlowClusterQC.ClusterQC]_38_38 /// The public keys associated with the Distributed Key Generation_38 /// process that consensus nodes participate in_38 /// Group key is the last element at index: length - 1_38 access(all) var dkgKeys: [String]_38}
Get Epoch Metadata
The FlowEpoch smart contract provides a public function, FlowEpoch.getEpochMetadata()
to query the metadata for a particular epoch.
You can use the Get Epoch Metadata(EP.01) script with the following arguments:
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| epochCounter | UInt64 | The counter of the epoch to get metadata for. |
Get Configurable Metadata
The FlowEpoch smart contract also has a set of metadata that is configurable by the admin
for phase lengths, number of collector clusters, and inflation percentage.
_17access(all) struct Config {_17 /// The number of views in an entire epoch_17 access(all) var numViewsInEpoch: UInt64_17_17 /// The number of views in the staking auction_17 access(all) var numViewsInStakingAuction: UInt64_17 _17 /// The number of views in each dkg phase_17 access(all) var numViewsInDKGPhase: UInt64_17_17 /// The number of collector clusters in each epoch_17 access(all) var numCollectorClusters: UInt16_17_17 /// Tracks the annualized percentage of FLOW total supply that is minted as rewards at the end of an epoch_17 /// Calculation for a single epoch would be (totalSupply * FLOWsupplyIncreasePercentage) / 52_17 access(all) var FLOWsupplyIncreasePercentage: UFix64_17}
You can use the Get Configurable Metadata(EP.02) script to get the list of configurable metadata:
This script does not require any arguments.
Get Epoch Counter
The FlowEpoch smart contract always tracks the counter of the current epoch.
You can use the Get Epoch Counter(EP.03) script to get the current epoch counter.
This script does not require any arguments.
Get Epoch Phase
The FlowEpoch smart contract always tracks the active phase of the current epoch.
_10access(all) enum EpochPhase: UInt8 {_10 access(all) case STAKINGAUCTION_10 access(all) case EPOCHSETUP_10 access(all) case EPOCHCOMMIT_10}
You can use the Get Epoch Phase(EP.04) script to get the current epoch phase.
This script does not require any arguments.